Explained: The different kinds of cruise control and how they work
Explained: The different kinds of cruise control and how they work

Hands-free driving may be a relatively new innovation – but foot-free driving has been around for decades. In fact, the first cruise control systems were installed over 60 years ago – and in many ways they operate identically to the systems found today.
But what exactly is cruise control? Put simply, it’s an automatic system which keeps your car at a constant speed with as little variation as possible. The inventor, Ralph Teetor, was said to have come up with the idea after a frustrating journey with his lawyer, who sped up and slowed down as he talked.
How do you use cruise control?

Cruise control is offered as standard equipment or at least as an optional extra on nearly every new car sold in the UK – though you may need to look a bit harder for it if buying an older vehicle. Basic systems are usually operated by a control either on the steering wheel or a steering column stalk.
Cruise control consists of an up/down (or +/-) control, as well as a ‘Set’ button, a ‘Recall’ button and sometimes an on/off button. The driver brings the car up to their desired speed, and if the system is switched on, pressing ‘Set’ will store that speed in the car’s memory.
The vehicle will then take control of the accelerator, keeping the car at the desired speed for as long the driver wants. Fine-tuning of the speed can be achieved with the +/- controls, and the target speed is often shown on a dashboard display.
The system is switched off in two ways – either with external input, such as the driver pressing the throttle or brake, or by using the on/off switch. At this point, the desired speed is still usually stored in the car’s memory, and that’s what the ‘Recall’ button is for – allowing the driver to return to their previous speed after passing an obstruction, junction or traffic.
What are the other kinds?
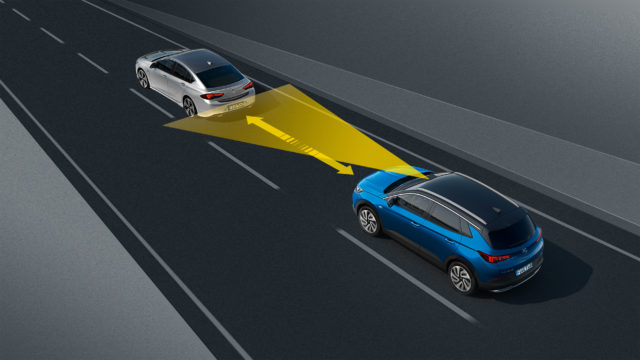
There’s not really much you can innovate on cruise control, but car manufacturers have managed to do it – and come out with adaptive cruise control and advanced adaptive cruise control.
Adaptive cruise control adds a scanner to the front of the car, usually a camera, radar, or laser array – or some combination of the three. This continuously scans the road ahead for traffic and is able to detect when there’s a car in front.
The system then alters your car’s speed so that instead of closing the gap to a slower-moving car, it will follow it at a set distance – controllable by the driver. The car will continue to match the speed of the car in front until it changes lane, exits the road or the driver overtakes.
Advanced adaptive cruise control adds an extra layer to this, as it’s capable of altering the cruise control’s speed limit to match the speed limit of the road it’s driving on – ensuring that the driver is never speeding.
Adaptive cruise control is usually paired with a form of autonomous emergency braking, and usually with lane-keeping assist, too. The most sophisticated systems will work at any speed – from following cars at high speeds on the motorway to crawling autonomously at the back of a queue of stop-start traffic. These systems are usually paired with an automatic gearbox, to prevent over- or under-revving by an inattentive driver. Cruise control in manual cars is usually disengaged when the clutch or gears are operated.
What are the advantages and disadvantages?
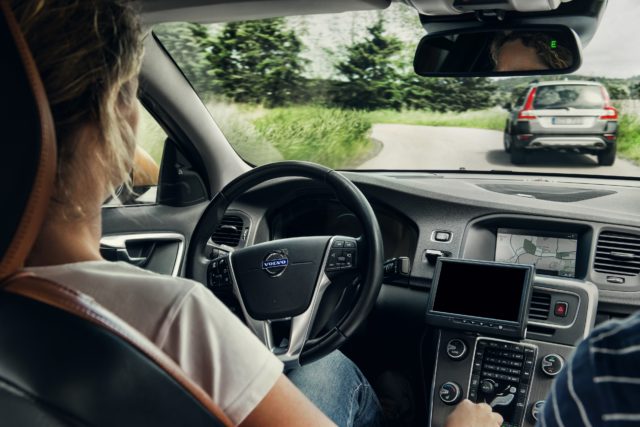

Cruise control has several advantages, chief among which is fatigue reduction. Allowing drivers to take their minds off keeping a constant speed allows them to focus more on steering and interacting with other traffic, as well as allowing them to stretch their legs and reduce muscle aches.
Advanced adaptive cruise control can prevent accidents thanks to its sensor array knowing where other vehicles are, and systems capable of reading speed limits can prevent drivers violating them and risking a ticket. It can also improve fuel efficiency.
However, it can be dangerous. Sophisticated systems, especially those paired with lane-keeping assistance tech, can encourage drivers to pay less attention when driving, increasing the risk of a collision.
Older systems were also very dangerous in the rain, on icy roads or on loose surfaces. That’s because the loss of traction in a wheel could lead the car to speed up rather than slow down, resulting in a total loss of control.





